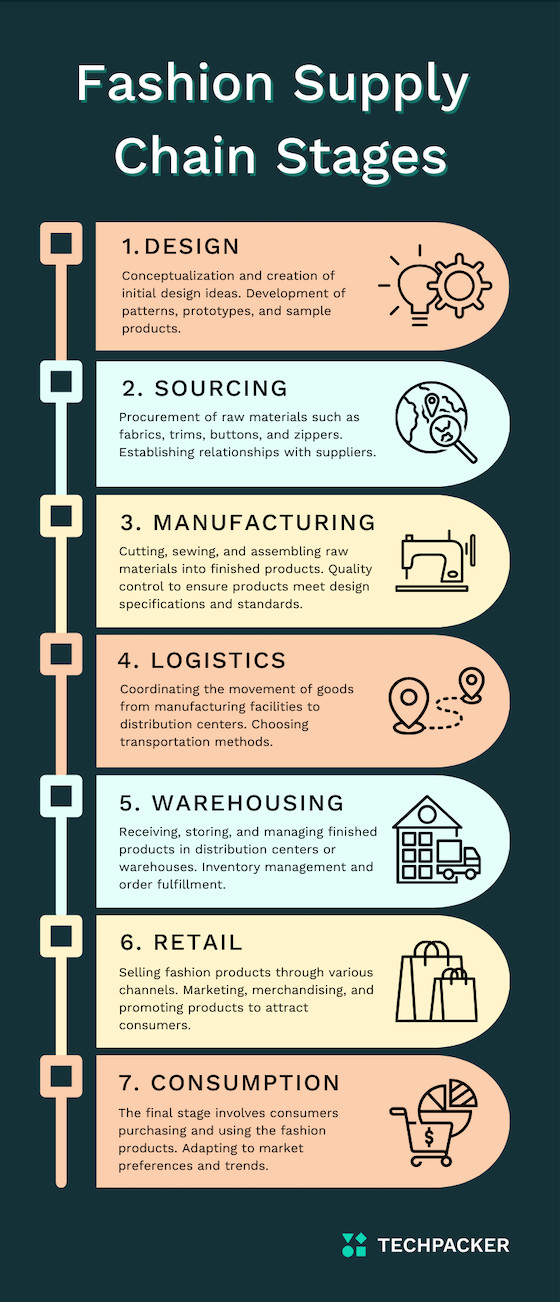
The fast fashion supply chain is a complex network designed for speed and responsiveness to rapidly changing trends. Its core principle is to minimize the time it takes for a garment to go from concept to consumer, often within weeks or even days. This requires a highly coordinated system involving design, production, distribution, and retail.
Fast fashion prioritizes speed and low costs. Design teams constantly monitor trends, quickly translating them into new styles. Production often occurs in countries with lower labor costs, utilizing efficient manufacturing techniques and large-scale production. Distribution centers are strategically located to facilitate rapid delivery to retail stores and online platforms. Technology plays a vital role in connecting these stages, enabling real-time communication and data sharing.
A key characteristic of the fast fashion supply chain is its reliance on short production cycles and frequent new arrivals. Rather than adhering to traditional seasonal collections, fast fashion brands continuously introduce new styles, keeping consumers engaged and encouraging frequent purchases. This constant influx of new products requires a flexible and agile supply chain capable of adapting to changing demands.
While speed and cost-effectiveness are central, the fast fashion model has faced increasing scrutiny regarding its environmental and social impact. The high volume of production and consumption contributes to textile waste and resource depletion. Concerns about labor practices in manufacturing facilities have also been raised. As a result, there’s a growing movement towards more sustainable practices within the fast fashion supply chain.
Transparency is often lacking in fast fashion supply chains. The complex network of suppliers and manufacturers can make it difficult to trace the origin of materials and monitor working conditions. Consumers are increasingly demanding greater transparency and ethical sourcing from fast fashion brands.
The fast fashion supply chain relies heavily on data and technology. Trend forecasting tools, inventory management systems, and logistics software enable efficient planning and execution. Real-time data visibility allows brands to react quickly to changes in demand and optimize production accordingly. E-commerce platforms play a crucial role in reaching consumers directly, further accelerating the speed of the supply chain.
Future developments in the fast fashion supply chain are likely to involve greater automation, further integration of technology, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. On-demand manufacturing, 3D printing, and AI-powered design tools could revolutionize production processes. Circular economy principles and sustainable material sourcing will become increasingly important to address environmental concerns.
The fast fashion supply chain represents a significant evolution in the fashion industry, enabling rapid response to trends and increased accessibility to fashionable clothing. However, addressing the environmental and social challenges associated with this model is crucial for its long-term sustainability. The future of fast fashion likely lies in finding a balance between speed, affordability, and responsible practices. Greater transparency, ethical sourcing, and sustainable production methods will be essential for the continued success of the fast fashion industry.