Fashion Sustainability Jobs are increasingly vital in today’s world, and mens-fashion.net is here to guide you. These roles are perfect for individuals passionate about merging style with environmental and ethical responsibility, offering a unique opportunity to make a significant impact. Ready to dive in? This comprehensive guide explores how you can find and thrive in fashion sustainability jobs, blending your love for fashion with a commitment to a better world.
1. What Exactly Are Fashion Sustainability Jobs?
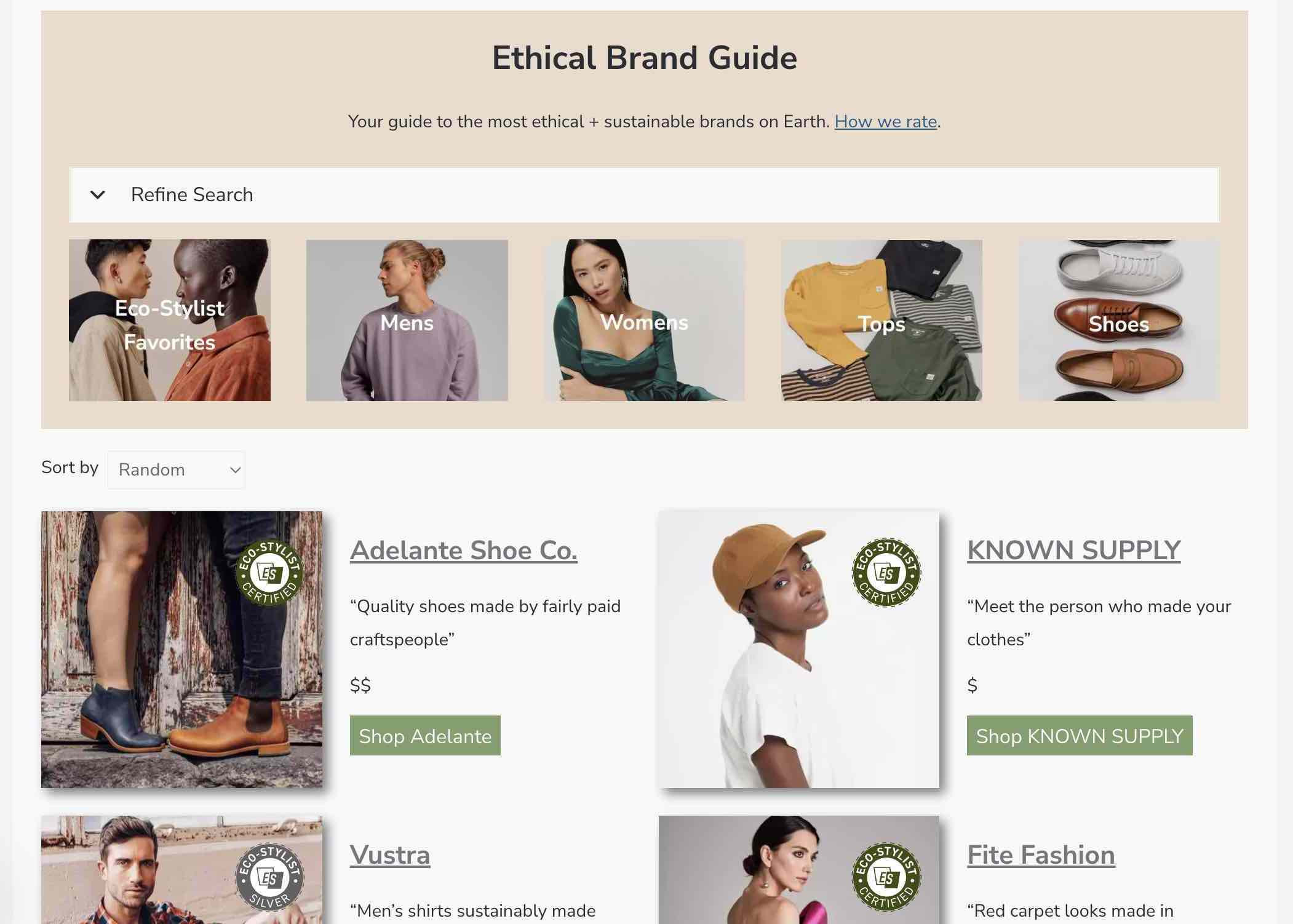
Fashion sustainability jobs involve roles focused on reducing the environmental and social impact of the fashion industry. These jobs are crucial for promoting ethical practices and sustainable innovation.
These roles span various areas, including:
- Sustainable Design: Creating eco-friendly clothing and accessories.
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring materials are sourced responsibly.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizing processes to reduce waste and emissions.
- Marketing and Communications: Promoting sustainable fashion to consumers.
- Research and Development: Innovating new sustainable materials and technologies.
Sustainable fashion jobs are essential for addressing the fashion industry’s negative impacts, which include pollution, waste, and unethical labor practices. A study by the Fashion Institute of Technology (FIT) in July 2025 highlighted that consumer demand for sustainable fashion is increasing, driving the need for more professionals in these roles.
1.1. Why is Sustainability Important in Fashion?
Sustainability in fashion is critical because the industry is a major polluter and contributor to social issues. The fashion industry is responsible for significant environmental damage, including water pollution from textile dyeing, greenhouse gas emissions from manufacturing and transportation, and textile waste ending up in landfills. Socially, the industry has faced criticism for poor working conditions and unfair wages in garment factories.
Sustainability aims to mitigate these issues through:
- Reducing Environmental Impact: Using eco-friendly materials, minimizing waste, and conserving resources.
- Ensuring Ethical Labor Practices: Providing fair wages, safe working conditions, and respecting workers’ rights.
- Promoting Transparency: Ensuring traceability and accountability throughout the supply chain.
- Educating Consumers: Raising awareness about the importance of sustainable choices.
1.2. What Skills Are Needed for Fashion Sustainability Jobs?
To excel in fashion sustainability jobs, you need a combination of technical and soft skills. Key skills include:
- Knowledge of Sustainable Materials: Understanding the properties and applications of eco-friendly fabrics and materials.
- Supply Chain Management: Managing and optimizing supply chains to ensure sustainability.
- Design Skills: Creating innovative and sustainable designs that minimize waste and environmental impact.
- Communication Skills: Effectively communicating sustainability initiatives to stakeholders.
- Analytical Skills: Analyzing data to measure and improve sustainability performance.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Addressing complex sustainability challenges and finding innovative solutions.
- Project Management: Managing sustainability projects and initiatives effectively.
1.3. What Are the Different Types of Fashion Sustainability Jobs?
The fashion industry offers a wide array of sustainability-focused roles, each with its unique responsibilities and contributions. Here are some prominent types of fashion sustainability jobs:
| Job Title | Description | Average Salary (USA) |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability Manager | Leads and implements sustainability strategies within a fashion company. | $85,000 |
| Sustainable Designer | Creates eco-friendly and ethically produced clothing and accessories. | $70,000 |
| Ethical Sourcing Manager | Ensures materials are sourced responsibly and ethically. | $78,000 |
| Supply Chain Sustainability Analyst | Analyzes and optimizes supply chain processes to reduce environmental impact. | $65,000 |
| Sustainability Marketing Specialist | Develops and implements marketing campaigns to promote sustainable fashion. | $60,000 |
| Textile Sustainability Researcher | Researches and develops new sustainable materials and technologies for the fashion industry. | $72,000 |
| Circular Economy Specialist | Focuses on creating closed-loop systems to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization. | $75,000 |
| Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Manager | Manages a company’s social responsibility initiatives, ensuring ethical and sustainable practices. | $82,000 |
| Environmental Compliance Officer | Ensures the company complies with environmental regulations and standards. | $70,000 |
| Sustainable Product Developer | Develops and innovates sustainable products, considering environmental and social impacts. | $68,000 |



Note: Salaries can vary widely based on experience, location, and company size.
2. Where Can You Find Fashion Sustainability Jobs?
Finding fashion sustainability jobs requires targeted research and networking. Here are some of the best resources to explore:
- Online Job Boards: Websites like LinkedIn, Indeed, and Glassdoor often list sustainability-related positions in the fashion industry.
- Specialized Sustainability Job Sites: Platforms like GreenBiz, Idealist, and SustainableBusiness.com focus specifically on sustainability roles.
- Fashion Industry Job Boards: Websites like Business of Fashion and WWD (Women’s Wear Daily) often feature sustainability positions.
- Company Websites: Check the career pages of fashion brands and retailers known for their sustainability initiatives.
- Networking: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with people working in sustainable fashion.
- Recruiting Agencies: Partner with recruiting agencies that specialize in sustainability and ethical fashion placements.
2.1. Top Websites for Sustainability Jobs
| Website | Focus |
|---|---|
| Professional networking and job postings, including many sustainability-related roles. | |
| Indeed | Extensive job listings, with filters to search for sustainability and ethical fashion positions. |
| Glassdoor | Job listings and company reviews, providing insights into company culture and salary expectations. |
| GreenBiz | A leading source for sustainability news and job opportunities. |
| Idealist | Focuses on nonprofit and social impact jobs, including many roles in sustainable fashion. |
| SustainableBusiness.com | Job board dedicated to sustainability positions across various industries. |
| Business of Fashion (BoF) | A leading fashion industry publication with a job board featuring sustainability roles. |
| Women’s Wear Daily (WWD) | Fashion industry news and job postings, including positions in sustainable fashion. |
| Common Objective (CO) | A professional network for the fashion industry that connects businesses and individuals focused on sustainability, offers job postings and networking opportunities. |
| Fashion United | International fashion news and jobs, including sustainability roles. |
2.2. How to Use LinkedIn for Job Searching
LinkedIn is a powerful tool for finding fashion sustainability jobs and connecting with industry professionals. Here’s how to maximize your LinkedIn presence:
- Optimize Your Profile: Use keywords like “sustainable fashion,” “ethical sourcing,” and “supply chain sustainability” in your headline, summary, and job descriptions.
- Network Strategically: Connect with professionals in sustainable fashion, join relevant groups, and participate in discussions.
- Search for Jobs: Use advanced search filters to find job postings that match your skills and interests. Set up job alerts to receive notifications when new positions are posted.
- Engage with Content: Share articles, comment on posts, and create your own content to showcase your expertise and passion for sustainability.
- Reach Out: Don’t hesitate to reach out to recruiters and hiring managers directly to express your interest in potential opportunities.
2.3. Networking Tips for the Fashion Industry
Networking is essential for landing a job in the competitive fashion industry. Here are some tips for effective networking:
- Attend Industry Events: Conferences, trade shows, and workshops provide opportunities to meet professionals and learn about the latest trends.
- Join Professional Organizations: Groups like the Sustainable Apparel Coalition and the Ethical Fashion Forum offer networking opportunities and resources.
- Informational Interviews: Reach out to people working in sustainable fashion and ask for informational interviews to learn about their experiences and get advice.
- Online Communities: Participate in online forums, social media groups, and professional networks to connect with like-minded individuals.
- Follow Up: After meeting someone, send a thank-you note or email to reinforce the connection and express your interest in staying in touch.
3. How to Prepare for a Career in Fashion Sustainability
Preparing for a career in fashion sustainability involves gaining the necessary education, skills, and experience. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you get started:
3.1. Education and Training Programs
Consider pursuing degrees or certifications in relevant fields such as:
- Fashion Design: Focus on sustainable design principles and eco-friendly materials.
- Environmental Science: Gain a strong understanding of environmental issues and sustainability practices.
- Supply Chain Management: Learn about sustainable supply chain strategies and ethical sourcing.
- Business Administration: Develop management and leadership skills with a focus on sustainability.
- Sustainability Studies: A multidisciplinary approach to understanding and addressing sustainability challenges.
Several universities and colleges offer specialized programs in sustainable fashion. According to the Fashion Institute of Technology (FIT), graduates with sustainability-focused degrees are highly sought after in the industry.
3.2. Internships and Volunteer Opportunities
Internships and volunteer positions are valuable for gaining practical experience and building your network. Look for opportunities at:
- Sustainable Fashion Brands: Work directly with companies committed to ethical and environmental practices.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Support initiatives promoting sustainable fashion and ethical labor practices.
- Research Institutions: Contribute to studies on sustainable materials and technologies.
- Supply Chain Companies: Gain experience in sustainable sourcing and supply chain optimization.
3.3. Building a Strong Resume and Portfolio
A well-crafted resume and portfolio are essential for showcasing your skills and experience to potential employers. Here are some tips:
- Highlight Relevant Skills: Emphasize your knowledge of sustainable materials, supply chain management, and design skills.
- Showcase Your Projects: Include examples of sustainable designs, research projects, and initiatives you have worked on.
- Quantify Your Achievements: Use numbers to demonstrate the impact of your work, such as reducing waste or improving ethical sourcing.
- Tailor Your Application: Customize your resume and cover letter to match the specific requirements of each job.
- Get Feedback: Ask mentors and career advisors to review your resume and portfolio and provide constructive criticism.
3.4. Developing Your Personal Brand
In today’s digital age, developing a strong personal brand is crucial for standing out in the job market. Here’s how to build your personal brand:
- Create a Professional Website: Showcase your resume, portfolio, and personal story.
- Engage on Social Media: Share your thoughts and ideas on sustainable fashion on platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Instagram.
- Write Blog Posts: Publish articles on topics related to sustainable fashion to demonstrate your expertise.
- Speak at Events: Volunteer to speak at conferences, workshops, and webinars to share your knowledge and passion.
- Network Online: Connect with industry professionals and participate in online discussions to build relationships.
4. Understanding the Current Trends in Sustainable Fashion
Staying informed about the latest trends in sustainable fashion is crucial for success in this dynamic field. Here are some key trends to watch:
4.1. Circular Economy
The circular economy is a model that focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization. In fashion, this means:
- Designing for Durability: Creating clothes that last longer and can be repaired.
- Using Recycled Materials: Utilizing recycled fabrics and materials to reduce the demand for virgin resources.
- Implementing Take-Back Programs: Allowing customers to return used clothes for recycling or resale.
- Promoting Clothing Rental and Resale: Encouraging consumers to rent or buy used clothing to extend the life cycle of garments.
4.2. Innovative Materials
The development of new sustainable materials is transforming the fashion industry. Some notable examples include:
- Recycled Polyester: Made from recycled plastic bottles, reducing waste and conserving resources.
- Organic Cotton: Grown without synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, minimizing environmental impact.
- Tencel (Lyocell): Made from sustainably sourced wood pulp using a closed-loop production process.
- Piñatex: Made from pineapple leaf fibers, providing a sustainable alternative to leather.
- Mylo: Made from mycelium (mushroom roots), offering a biodegradable and cruelty-free leather alternative.
4.3. Transparency and Traceability
Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency and traceability in the fashion supply chain. This involves:
- Supply Chain Mapping: Tracking the journey of a garment from raw materials to finished product.
- Certifications: Verifying that products meet certain environmental and social standards through certifications like GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) and Fair Trade.
- Blockchain Technology: Using blockchain to track and verify the authenticity and sustainability of products.
- Consumer Education: Providing consumers with information about the environmental and social impact of their clothing.
4.4. Ethical Production
Ethical production ensures fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for workers’ rights. This involves:
- Fair Labor Practices: Ensuring that garment workers are paid a living wage and have access to safe working conditions.
- Worker Empowerment: Supporting worker-led initiatives and organizations that advocate for fair labor practices.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Regularly auditing factories to ensure compliance with labor standards.
- Transparency: Disclosing information about factories and suppliers to promote accountability.
5. Thriving in Fashion Sustainability Jobs
Once you land a job in fashion sustainability, it’s important to continue learning and growing in your role. Here are some tips for thriving in your career:
5.1. Continuous Learning and Development
- Stay Updated: Follow industry news, attend conferences, and participate in webinars to stay informed about the latest trends and best practices.
- Take Courses: Enroll in online courses and workshops to enhance your skills and knowledge in areas like sustainable design, supply chain management, and marketing.
- Read Books and Articles: Stay up-to-date on the latest research and thought leadership in sustainable fashion by reading books and articles from reputable sources.
- Join Professional Networks: Participate in professional organizations and online communities to connect with peers and learn from their experiences.
5.2. Building Relationships and Collaborating
- Network: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with people working in sustainable fashion.
- Collaborate: Work with colleagues, suppliers, and stakeholders to implement sustainability initiatives and achieve common goals.
- Communicate: Effectively communicate your ideas and findings to stakeholders, and be open to feedback and suggestions.
- Mentor: Offer guidance and support to junior colleagues and students who are interested in pursuing careers in sustainable fashion.
5.3. Innovating and Problem-Solving
- Think Creatively: Look for innovative solutions to sustainability challenges and be open to new ideas and approaches.
- Experiment: Try new materials, technologies, and processes to improve sustainability performance.
- Analyze Data: Use data to identify trends, measure progress, and inform decision-making.
- Learn from Mistakes: Don’t be afraid to take risks and learn from your mistakes, and use these lessons to improve your future performance.
5.4. Advocating for Change
- Raise Awareness: Educate colleagues, customers, and stakeholders about the importance of sustainable fashion and the benefits of ethical practices.
- Influence Policy: Advocate for policies that support sustainable fashion and promote ethical labor practices.
- Support Sustainable Brands: Patronize brands that are committed to sustainability and ethical production.
- Lead by Example: Demonstrate your commitment to sustainability through your own actions and choices.
6. The Future of Fashion Sustainability Jobs
The future of fashion sustainability jobs is bright, with increasing demand for professionals who can drive positive change in the industry. As consumers become more aware of the environmental and social impacts of fashion, they are demanding more sustainable and ethical products. This trend is driving companies to invest in sustainability initiatives and hire professionals who can help them achieve their goals.
6.1. Growing Demand for Sustainability Professionals
According to a report by McKinsey & Company, the sustainable fashion market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, creating new opportunities for sustainability professionals. The report highlights that consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for sustainable products, and companies that prioritize sustainability are likely to outperform their competitors.
6.2. Emerging Technologies and Innovations
Emerging technologies and innovations are transforming the fashion industry and creating new opportunities for sustainability professionals. Some notable examples include:
- 3D Printing: Enables the creation of custom-fit clothing and reduces waste by producing only what is needed.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Can be used to optimize supply chains, predict consumer demand, and personalize marketing messages.
- Blockchain: Can be used to track and verify the authenticity and sustainability of products.
- Nanotechnology: Can be used to create fabrics that are water-resistant, stain-resistant, and antimicrobial.
6.3. The Role of Policy and Regulation
Policy and regulation are playing an increasingly important role in promoting sustainability in the fashion industry. Governments around the world are implementing new laws and regulations to address issues such as textile waste, water pollution, and unethical labor practices. These policies are creating new opportunities for sustainability professionals who can help companies comply with regulations and implement sustainable practices.
6.4. Opportunities for Entrepreneurs and Innovators
The sustainable fashion industry is ripe with opportunities for entrepreneurs and innovators who can develop new solutions to sustainability challenges. Some potential areas for innovation include:
- Sustainable Materials: Developing new eco-friendly fabrics and materials that reduce environmental impact.
- Circular Economy Models: Creating closed-loop systems that minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
- Technology Solutions: Developing apps and platforms that help consumers make more sustainable choices.
- Ethical Production Methods: Implementing fair labor practices and supporting worker empowerment initiatives.
7. Success Stories in Fashion Sustainability
Learning from success stories can inspire and guide your journey in fashion sustainability. Here are a few examples of companies and individuals making a significant impact:
7.1. Patagonia
Patagonia is a well-known brand committed to environmental sustainability. The company uses recycled materials, promotes fair labor practices, and donates a percentage of its sales to environmental organizations. Patagonia’s commitment to sustainability has earned it a loyal customer base and a reputation as a leader in the industry.
7.2. Eileen Fisher
Eileen Fisher is a fashion designer and entrepreneur who has built a successful brand based on sustainable and ethical principles. The company uses organic and recycled materials, implements a take-back program, and supports worker empowerment initiatives. Eileen Fisher’s commitment to sustainability has earned her numerous awards and accolades.
7.3. Stella McCartney
Stella McCartney is a fashion designer who is known for her commitment to sustainability and animal rights. The company uses organic cotton, recycled polyester, and other sustainable materials, and it does not use leather, fur, or feathers in its products. Stella McCartney’s commitment to sustainability has made her a role model for other designers and brands.
7.4. Examples of Individuals Driving Change
- Carry Somers: Co-founder of Fashion Revolution, a global movement that advocates for greater transparency and accountability in the fashion industry.
- Orsola de Castro: Co-founder of Fashion Revolution and a leading voice in the sustainable fashion movement.
- Patrick Duffy: Founder of Global Fashion Exchange, an organization that promotes clothing swaps and recycling events.
- Dana Thomas: Author of “Fashionopolis: The Price of Fast Fashion and the Future of Clothes,” a book that examines the environmental and social impacts of the fashion industry.
8. Resources and Tools for Fashion Sustainability Professionals
There are numerous resources and tools available to support fashion sustainability professionals. Here are some of the most valuable:
8.1. Industry Associations and Organizations
- Sustainable Apparel Coalition (SAC): An industry-wide group of over 250 leading apparel, footwear, and textile brands, retailers, manufacturers, and organizations working to reduce the environmental and social impacts of their products.
- Ethical Fashion Forum (EFF): A global community of fashion professionals working to create a more sustainable and ethical fashion industry.
- Textile Exchange: A nonprofit organization that promotes the use of organic cotton and other sustainable materials.
- Fashion Revolution: A global movement that advocates for greater transparency and accountability in the fashion industry.
- Remake: A community of fashion lovers, activists, and brands fighting for fair wages and climate justice.
8.2. Online Courses and Certifications
- Sustainable Fashion Academy: Offers online courses and certifications in sustainable fashion.
- Centre for Sustainable Fashion: Provides education and training in sustainable fashion.
- edX and Coursera: Offer a variety of courses on sustainability, environmental science, and business.
- GOTS Certification: Certifies that textiles meet certain environmental and social standards.
- Fair Trade Certification: Ensures that products are produced in accordance with fair labor practices.
8.3. Books and Publications
- “Fashionopolis: The Price of Fast Fashion and the Future of Clothes” by Dana Thomas: Examines the environmental and social impacts of the fashion industry.
- “To Die For: Is Fashion Wearing Out the World?” by Lucy Siegle: Explores the environmental and social costs of fast fashion.
- “Overdressed: The Shockingly High Cost of Cheap Fashion” by Elizabeth Cline: Investigates the impact of fast fashion on consumers and the environment.
- “Sustainable Fashion: Past, Present and Future” by Jennifer Farley Gordon and Colleen Hill: Provides a comprehensive overview of the history, present, and future of sustainable fashion.
8.4. Software and Tools
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Software: Used to assess the environmental impacts of products throughout their life cycle.
- Supply Chain Mapping Tools: Help companies track and map their supply chains to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Data Analytics Software: Used to analyze data and measure sustainability performance.
- Project Management Software: Helps companies manage sustainability projects and initiatives effectively.
9. Addressing Common Challenges in Fashion Sustainability
While the field of fashion sustainability offers tremendous opportunities, it also presents several challenges. Being aware of these challenges and developing strategies to overcome them is crucial for success.
9.1. Cost and Affordability
Sustainable fashion often comes at a higher cost due to the use of eco-friendly materials, ethical labor practices, and sustainable production methods. This can make it challenging to compete with fast fashion brands that offer cheaper products.
Strategies to Address This Challenge:
- Educate Consumers: Raise awareness about the value of sustainable fashion and the long-term benefits of investing in quality, ethically produced garments.
- Innovate Sustainable Materials: Develop new sustainable materials that are cost-competitive with conventional materials.
- Optimize Production Processes: Implement efficient production processes to reduce costs without compromising sustainability.
- Promote Circular Economy Models: Encourage clothing rental, resale, and recycling to extend the life cycle of garments and reduce waste.
9.2. Greenwashing
Greenwashing is the practice of making false or misleading claims about the sustainability of products or practices. This can mislead consumers and undermine trust in the sustainable fashion industry.
Strategies to Address This Challenge:
- Demand Transparency: Advocate for greater transparency in the fashion supply chain, including information about materials, production processes, and labor practices.
- Verify Claims: Look for certifications and labels that verify the sustainability of products.
- Support Independent Research: Fund and promote independent research to evaluate the sustainability of different materials and practices.
- Hold Companies Accountable: Call out companies that engage in greenwashing and demand greater accountability.
9.3. Lack of Awareness and Education
Many consumers are not aware of the environmental and social impacts of the fashion industry and may not understand the importance of sustainable fashion.
Strategies to Address This Challenge:
- Educate Consumers: Provide consumers with information about the environmental and social impacts of fashion and the benefits of sustainable choices.
- Partner with Influencers: Collaborate with influencers and bloggers to promote sustainable fashion and reach a wider audience.
- Create Engaging Content: Develop engaging content that highlights the stories behind sustainable brands and products.
- Offer Educational Programs: Provide educational programs and workshops to help consumers learn about sustainable fashion.
9.4. Scalability
Scaling up sustainable practices and initiatives can be challenging, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that may lack the resources and infrastructure to implement sustainable practices.
Strategies to Address This Challenge:
- Collaboration: Partner with other companies and organizations to share resources and expertise.
- Technology Adoption: Adopt new technologies and innovations that can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Government Support: Advocate for government policies that support sustainable businesses and promote sustainable practices.
- Access to Funding: Seek funding from investors and organizations that support sustainable businesses.
10. FAQ About Fashion Sustainability Jobs
1. What are the key responsibilities of a Sustainability Manager in the fashion industry?
A Sustainability Manager leads and implements sustainability strategies, ensuring ethical sourcing, reducing environmental impact, and promoting sustainable practices throughout the company.
2. How can I gain practical experience in sustainable fashion if I’m a student?
Seek internships with sustainable brands, volunteer for nonprofit organizations focused on ethical fashion, and participate in relevant research projects to gain hands-on experience.
3. Which certifications are most valuable for professionals in sustainable fashion?
GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) and Fair Trade certifications are highly valued, as they verify adherence to environmental and social standards in textile production.
4. What are some emerging trends in sustainable materials for fashion?
Emerging trends include the use of recycled polyester, organic cotton, Tencel (Lyocell), Piñatex (pineapple leaf fiber), and Mylo (mushroom-based leather alternative).
5. How can blockchain technology contribute to fashion sustainability?
Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability by tracking and verifying the authenticity and sustainability of products throughout the supply chain.
6. What are the main challenges in making sustainable fashion more affordable?
The higher costs associated with eco-friendly materials, ethical labor practices, and sustainable production methods pose significant challenges.
7. How can consumers identify and avoid greenwashing in the fashion industry?
Look for verified certifications, demand supply chain transparency, and support independent research to evaluate the sustainability claims of products.
8. What role does policy and regulation play in promoting sustainable fashion?
Government policies and regulations can incentivize sustainable practices by addressing textile waste, water pollution, and unethical labor, thus fostering industry-wide change.
9. What are some innovative solutions for scaling up sustainable practices in the fashion industry?
Collaboration among companies, adoption of new technologies, government support, and access to funding are key to scaling sustainable practices effectively.
10. What skills are most needed for fashion sustainability jobs in 2024?
In 2024, you’ll need expertise in sustainable materials, supply chain management, innovative design, communication, data analytics, problem-solving, and project management.
Conclusion
Fashion sustainability jobs offer a rewarding career path for individuals passionate about making a positive impact on the environment and society. By gaining the necessary education, skills, and experience, you can thrive in this growing field and contribute to a more sustainable and ethical fashion industry. Stay informed about the latest trends, build relationships, and continue learning and innovating to succeed in your career. Mens-fashion.net is your go-to resource for staying ahead in the dynamic world of men’s fashion.
Ready to take the next step? Explore mens-fashion.net for more insights, tips, and resources to elevate your style and career in sustainable fashion. Discover the latest trends, get expert advice, and find the perfect inspiration to express your unique style while contributing to a better world. Visit mens-fashion.net today and unlock your potential in the world of sustainable fashion!
Address: 227 W 27th St, New York, NY 10001, United States.
Phone: +1 (212) 217-5800.
Website: mens-fashion.net.

